A
Adhesive Test
One of the most common tests for consumer goods inspections. It verifies the resistance of the logo and other labels/marks to daily use by applying 3M tape onto them and then removing the tape. If the logo peels off, there is a high risk that the printed information will disappear quickly.
Acceptance Number
The acceptance number is the maximum number of defects or defective units in the sample that will permit acceptance lot or batch. For example, if the acceptance number is 5, and the number of defects is five or less, the batch will pass. If there are six defects, the batch fails.
Acceptance Sampling
Acceptance Sampling is used to decide whether to accept or reject a production lot. After selecting the samples from a production lot, we inspect the units. Then count how many defects are found among the samples and we use the result (number of defects found versus maximum number of defects allowed) to decide whether to accept or reject the lot.
Acceptable Quality Level (AQL)
The acceptable quality level (AQL) is based on the standard MIL-STD-105E / ISO 2859-1. It represents the maximum percent of defects acceptable in a production run. (or the maximum number of defects per hundred units). This definition has since been changed to Acceptable Quality.
The AQL has two different definitions due to standard changes.
1. Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) / MIL-STD-105E / ISO 2859-1 (1999)
The Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) is defined as the maximum percent defective (or the maximum number of defects per hundred units) that, for purpose of sampling inspection, can be considered satisfactory as a process average. The sampling plans most frequently used by the department of Defense are based on the AQL.
2. Acceptance Quality Limit / ANSI/ASQC Z1.4-2003
The AQL is the quality level that is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling.
The following note on the meaning of AQL was introduced with the ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-2003 revision.
The concept of AQL only applies when an acceptance sampling scheme with rules for switching between normal, tightened and reduced inspection and discontinuance of sampling inspection is used. These rules are designed to encourage suppliers to have process averages consistently better than the AQL. If suppliers fail to do so, there is a high probability of being switched from normal inspection to tightened inspection where lot acceptance becomes more difficult. Once on tightened inspection, unless corrective action is taken to improve product quality, it is very likely that the rule requiring discontinuance of sampling inspection will be invoked.
Although individual lots with quality as bad as the AQL can be accepted with fairly high probability, the designation of an AQL does not suggest that this is necessarily a desirable quality level. The AQL is a parameter of the sampling scheme and should not be confused with a process average which describes the operating level of a manufacturing process. It is expected that the product quality level will be less than the AQL to avoid excessive non accepted lots.
The AQL values are defined as percent nonconforming or defects or nonconformities per hundred units.
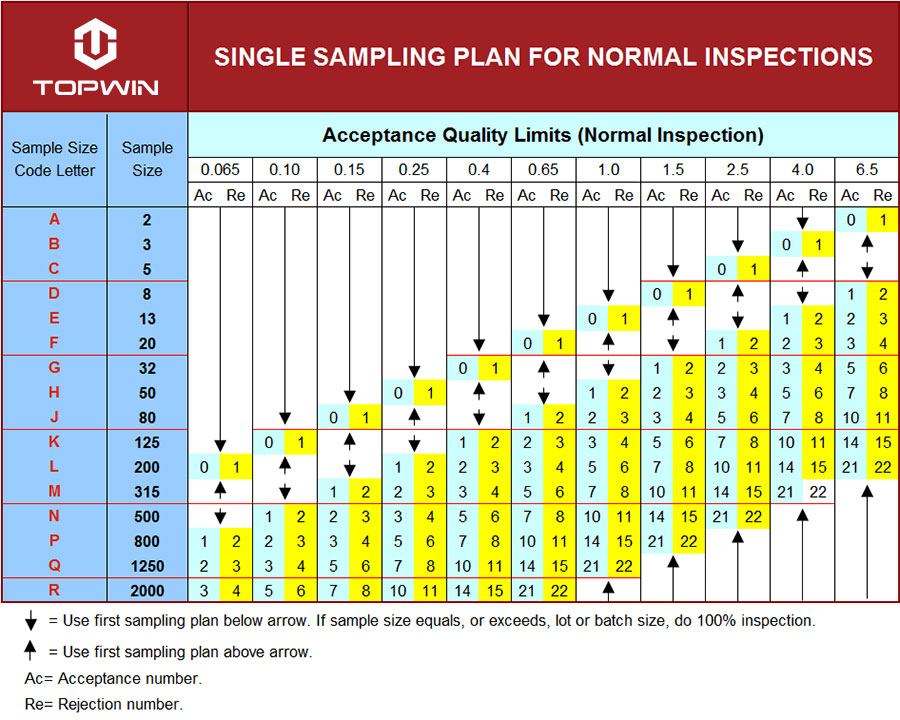
Acceptance Quality Limit
AQL is now Acceptance Quality Limit in most standards. It defines the quality level that is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling.
It is the limit of defects that the customer is prepared to accept. For example – I want no more than 2.5% of defective product units in the total order. In this case, the AQL is 2.5%.
The following note on the meaning of AQL was introduced with the ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-2003. revision: The concept of AQL only applies when an acceptance sampling scheme with rules for switching between normal, tightened, and reduced inspection and discontinuance of sampling inspection are used. These rules are designed to encourage suppliers to have process averages consistently better than the AQL. If suppliers fail to do so, there is a high probability of being switched from normal inspection to tightened inspection where lot acceptance becomes more difficult.
Accreditation
Accreditation is granted by governmental or internationally recognized organizations. It validates the ability of a third-party quality control company to perform inspection services with integrity, objectivity, and expertise.
Accredited laboratory
An accredited laboratory is officially recognized as able to perform specific types of testing, measurement, and calibration. They are seen to be reliable and professional and will issue valid test certificates acceptable to Customs at your product’s destination.
Appearance check
An appearance check is one of the most basic controls performed during an inspection. It aims to verify the product’s general aspect and looks for defects mainly related to weak manufacturing processes and in-line quality control problems.
Approval sample
An approval sample, also called a ‘golden sample,’ ‘pre-production sample’ or ‘PP-sample,’ is usually sent by the buyer to the third-party inspection company and manufacturer. It is the reference product that will be compared to the production samples. The production and approval samples should be very similar. An inspection report will point out the differences.
Assessment
An assessment evaluates the level of compliance of products against specific quality standards. The evaluation process includes observation, data collection, and analysis.
Audit
An audit is the inspection of a manufacturer by a third-party organization to verify compliance with your standards and/or international standards such as ISO 9001, SA8000, ISO 14000.
B
Batch/Lot
A batch or lot is a collection of products which are identical in size and type, which have been produced under similar conditions, at the same time.
C
Certification
Certification is the delivery of an official document by notified bodies (laboratories for our industry) to attest the compliance of a specific consumer good to particular standards and regulations of interest to the buyer.
Checklist
A checklist is a list of checkpoints referred to when performing an inspection or a supplier audit. It helps to ensure all relevant aspects of the product, or the factory are assessed to determine the level of control.
Conformity
Compliance of manufactured goods to product specifications, acceptable quality limits (AQL’s,) and standards.
Consumer quality standards
All aspects of quality that are relevant from a consumer’s point of view and which allow them to assess the quality of a product.
Corrective action
Corrective actions are improvements which eliminate nonconformities by addressing the root cause of a problem. They ensure quality objectives are reached and similar issues are avoided in the future.
Cosmetic check
The control of all physical aspects of a product.
Consumer safety
Everything that is put in place to protect consumers and prevent them from being harmed by defective workmanship.
Container Loading Supervision (CLS)
This inspection is performed at the manufacturer’s warehouse or at the forwarder’s premises. The aim of this inspection is to verify your products, the quantity of goods, and the loading process.
This inspection includes:
- An inspection of the container before the loading (container condition)
- An inspection of your products (product check according to your P/O: quantity, appearance, and general quality)
- An inspection of the loading process (cartons conditions, filling-up level etc.)
Continuous Sampling Plan
A continuous sampling is appropriate for processes that deliver a continuous flow of a product rather than batches. In this plan, we begin by inspecting 100 % of the units coming from the process. After a certain number of items inspected show no defects, the sampling decreases to a fraction of the items. The decreased sampling continues until we find a nonconforming unit. At that point, the plan reverts to 100 % inspection and follows the same pattern.
Cost of Poor Quality
Costs of poor quality are the extra expenses caused by delivering poor quality goods to customers. These expenses have two sources: internal failure costs (from defects identified before customers get the product) and external failure costs (costs incurred after a customer receives the poor product or service). Defect sorting, rework, repairs, damage to a brand’s reputation and loss of client confidence are just a few examples of costs associated with poor quality.
Cost of Quality
This refers to all costs involved in the prevention of quality issues, defects, assessments of process performance, and measurement of financial consequences. Cost of quality is the cost justification of quality efforts. Cost of quality should be seen as an investment more than a cost.
Coverage area
The countries, regions, and cities where inspection and audit services can be performed.
Critical defect
A critical defect is one that, based on experience, is judged to be likely to result in hazardous or unsafe conditions for individuals using, maintaining, or depending upon the products; or will prevent the performance of a tactical function of a major end item. A critical defective is a unit of product that contains one or more critical defects. You can provide your own list of critical defects for an inspection. TOPWINs’ default AQL for critical defects is 0.
D
Defects Classification
The importance of workmanship defects varies depending on the specific defect size, its position, and the specification. Defects are systematically placed into subcategories to obtain a better insight into the overall quality of workmanship. The subcategories are generally labeled: Critical, Major, Minor.
Defects And Defectives
A defect is any nonconformance of the unit of product with the specified requirements. A defective is a unit of product which contains one or more defects. Failure to meet requirements with respect to quality characteristics are usually described in terms of defects or defectives.
Critical – A critical defect is on that judgment and experience indicate is likely to:
a. Result in hazardous or unsafe conditions for individuals using, maintaining, or depending upon the products; or
b. Prevent performance of the tactical function of a major end item. A critical defective is a unit of product that contains one or more critical defects.
You can provide your own list of Critical Defects to be inspected. TOPWIN’s default Critical Defect AQL is Not Allowed.
Major – A major defect is one, other than critical, that is likely to result in failure, or to reduce materially the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose. A major defective is a unit of product that contains one or more major defects.
You can provide your own list of Major Defects to be inspected. TOPWIN’s default Major Defect AQL is 2.5.
Minor – A minor defect is one that is not likely to reduce materially the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose or is a departure from established standards having little bearing on the effective use or operation of the unit of product. A Minor defective is a unit of product that contains one or more minor defects.
You can provide your own list of Minor Defects to be inspected. TOPWIN’s default Major Defect AQL is 4.0.
Defects per Hundred Units
The number of defects per hundred units of any given quantity units of product is one hundred times the number of defects contained therein (one or more defects being possible in any unit of product) divided by the total number of units of product, i.e.: Defects per hundred units = (Number of defectives x 100) / (number of units inspected)
Double Sampling Plan
A double sampling plan is a technique which inspects a batch in two stages, potentially saving time and money when large lots are involved. Initially, a sample of size n1 is taken from the lot and inspected. The results of the inspection lead to either acceptance or rejection based on set criteria. If it is rejected, a second sample of size n2 is taken and inspected. The results of the second inspection led to a final decision on whether to accept or reject the lot.
Directives
Directives are product specifications or properties required by official entities, governments, or trade unions. They must be fulfilled in order to sell the goods within the country.
Drawing of Samples
The foundation of sampling inspection is the assurance that a sample selected from a quantity of units represents the quality of that entire lot. Hence, the procedure used to select units from a lot must be such that it assures a sample free of bias.
During Production Inspection (DPI)
The inspection takes place when about 20% to 60% of the production has been completed. The aim is to ensure that contractual obligations regarding specifications, packaging, packing, and marking are met and to check if the factory will be able to respect the production schedule. If recommendations have been given during an Initial Production Inspection (IPI), the During Production Inspection determines whether these corrective action plan has been successfully implemented.
E
Expression of Nonconformance
The extent of nonconformance of product shall be expressed either in terms of percent defective or in terms of defects per hundred units (DHU).
F
Fail result
A fail result is a consequence of identifying at least one non-conformity outside the tolerance level defined by the buyer.
Factory Audit
A factory audit is the inspection of a manufacturer by a third-party organization to verify compliance with your standards and/or international standards such as ISO 9001, SA8000, ISO 14000. It covers the profile of the supplier, internal organization, safety regulations, quality processes, performance, delivery terms, and R&D. The audit also includes extensive worker and manager interviews in the factory worker’s language.
First-Articles Inspection (FAI)
The Initial Production Inspection is performed at the very first stage of the mass production. TOPWIN Inspectors will inspect the quality of the material and components used in the production process and make sure it fits your requirements and is according to your approved sample. It also includes a visual check on the quality of packing materials and accessories. The inspector will also monitor the assembly process and check the first production run.
The Initial Production Inspection ensures that the customer’s specifications are well-understood by the supplier/factory. The IPI will detect production discrepancies very early in the production processes; you will thus be able to take corrective actions sooner than later, saving time and securing your business.
I
In-process Quality Control (IPQC)
IPQC is the on-line inspection of products during production to confirm product compliance and reduce the risk of substandard quality and works. IPQC occurs at all stages of the process from raw material to pre-shipment.
Inspection
Inspection is the process of measuring, examining, testing, or otherwise comparing a unit of product with the requirements.
Inspection by Attribute
Inspection by attributes is inspection whereby either the unit of product is classified simply as defective or non-defective, or the number of defects in the unit of product is counted, with respect to a given requirement or set of requirements.
Inspection checklist
An Inspection checklist is a document which lists all the points an inspector should check during an inspection. The objective is to avoid missing important details.
Inspection Certificate
An inspection certificate is an official document that certifies that the quality of goods has been confirmed to meet requirements. It is necessary when a letter of credit is involved with releasing payment.
Inspection Cost
The Inspection cost is determined based on the time needed to perform the service. The unit of reference is called a “man-day.”
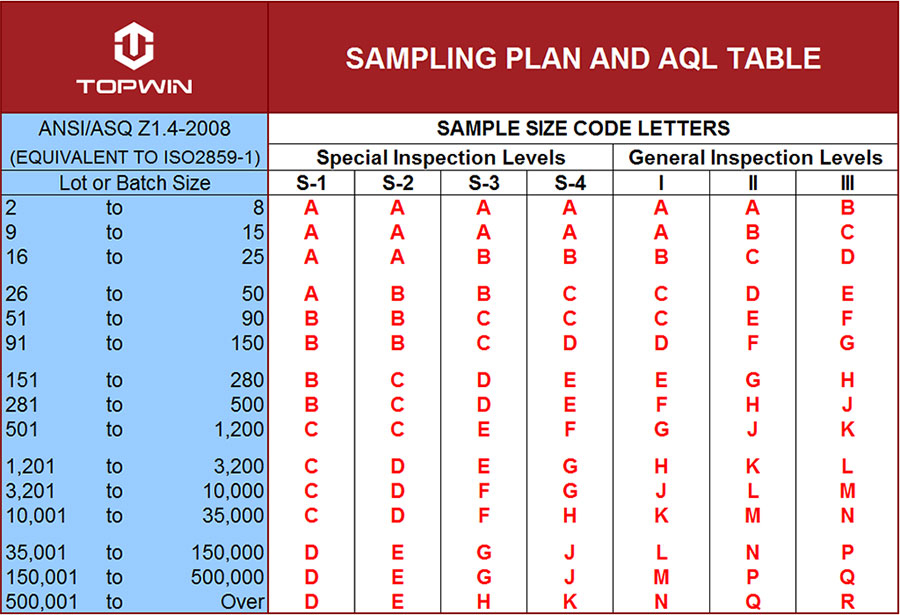
Inspection Levels
The standards provide for three general inspection levels and four special inspection levels. These seven levels permit the user to balance the cost of inspection against the amount of protection required.
Inspection protocol
An inspection protocol defines all the processes and steps involved in performing the inspection. It includes the list of the details to check.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property refers to ideas and inventions. For example, new designs, products, logos, and packaging which are unique.
IPQC/QA
Refers to In-Process Quality Control and Quality Assurance.
ISO
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the world’s largest developer of voluntary International Standards. International Standards give state of the art specifications for products, services, and good practice, helping to make industry more efficient and effective. Developed through global consensus, they help to break down barriers to international trade.
ISO is a network of national standards bodies. These national standards bodies make up the ISO membership and they represent ISO in their country.
Today ISO has members from 164 countries and 3335 technical bodies to take care of standard development. More than 150 people work full time for ISO’s Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland.
ISO 9000 Standards: this is a set of quality standards developed in 1987 by the International Organization for Standardization. The three major areas of certification are as follows:
ISO 9001: covers all the processes of a company from design and development to procurement, production, testing, installation, and service.
ISO 9002: covers everything except design and development.
ISO 9003: covers only inspection and testing.
ISO 9000
It is a set of international standards for quality management and quality assurance developed to help companies effectively document the quality system elements to be implemented to maintain an efficient quality system. They are not specific to any one industry and can be applied to organizations of any size. The ISO 9000 [link: http://asq.org/learn-about-quality/iso-9000/overview/overview.html] family contains these standards:
ISO 9001:2015: Quality management systems – Requirements
ISO 9000:2015: Quality management systems – Fundamentals and vocabulary (definitions)
ISO 9004:2009: Quality management systems – Managing for the sustained success of an organization (continuous improvement)
ISO 19011:2011: Guidelines for auditing management systems
Individuals and organizations cannot be certified to ISO 9000. ISO 9001 is the only standard within the ISO 9000 family to which organizations are certified.
L
Laboratory testing
All tests performed in a controlled environment to verify the safety and conformity of consumer goods to regulations and standards required in specific destination countries.
Letter of Credit
A letter of credit is a contract that provides a safe payment method protecting buyers and suppliers. It stipulates the conditions under which a payment can be released from the buyer’s bank account to the supplier’s. This contract is prepared by the buyer and the supplier and presented to the bank for validation. A letter of credit usually requires an inspection certificate for the release of payment.
Lot or Batch
The term lot or batch shall mean “inspection lot” or “inspection batch” i.e., a collection of units of product from which a sample is to be drawn and inspected to determine conformance with the acceptance criteria, any may differ from a collection of units designated as a lot or batch for other purposes (e.g., production, shipment, etc.).
M
Major defect
A major defect is one, that is likely to result in failure, or to materially reduce the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose. It is less serious than a critical defect. A major defective is a unit of product that contains one or more major defects. You can provide your own list of Major Defects to be inspected. TOPWIN’s default AQL for major defects is 2.5.
Man-day
A man-day is the unit of value used by inspection companies to estimate the cost of an inspection. It represents a working day spent by a Quality Controller (or Quality Inspector) to perform an inspection.
Manufacturer
A manufacturer is an entity with facilities, workforce, and machinery that allows them to make goods on a large scale.
Manufacturing
The action of producing goods by industrial processes.
Minor defect
A minor defect is one that is not likely to materially reduce the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose or is a departure from established standards having little bearing on the effective use or operation of the unit of product. A Minor defective is a unit of product that contains one or more defects. You can provide your own list of Minor Defects to be inspected. TOPWIN’s default AQL for minor defects is 4.0.
N
Nonconformance
A nonconformance may be defined as the failure of a unit of product to conform to specified requirements for any stated quality characteristic. The extent of nonconformance of product to the required quality characteristics shall be expressed either in terms of percent defective or in terms of defects per hundred units (DHU).
Normal Inspection
Normal inspection is used where there is no evidence that the quality of the product is likely to be better or worse than the specified quality level.
Notified body
A notified body is an entity that has been accredited by a country, or a trade union, to assess whether a product to be sold on the market meets the required standards.
O
Online Quality Management system/technology/software
Technology that allows you to manage and monitor quality control actions on your goods easily. In term of operations, it is a tool to ensure the efficient coordination and follow-up of all inspections and audits. In addition, advanced systems facilitate an in-depth analysis of the inspection results to enable benchmarking of suppliers and monitoring of their performance over time.
Operations
Normal inspection is used where there is no evidence that the quality of the product is likely to be better or worse than the specified quality level.
P
Payment term
The payment term defines when, how, and where the payment of goods from the buyer to the supplier should be made. The terms of payment include details of any deposit, the period for payment before or after the delivery of goods, and more.
Pass result
A pass result occurs when zero non-conformities are identified, or the number of non-conformities is within the tolerance level defined by the buyer.
Pending result
A pending result occurs when the buyer does not specify non-conformities, or they are not considered to have a direct consequence on sales.
Percent defective
The percent defective of any given quantity of units of product is one hundred times the number of defective units of product contained therein divided by the total number of units of product, i.e.: Percent defective = number of defectives x100 / number of units inspected.
Pre Shipment Inspection (PSI)
Also called Final Random Inspection (FRI), it is the most common inspection, and it is performed when at least 80% of the goods ordered are packed into export cartons. Samples are selected randomly, according to sampling standards and procedures and will be inspected according to your specifications, requirements and according to our protocols and expertise.
This inspection ensures that the production is in accordance with the specifications, purchase orders or letters of credit. It covers product appearance, workmanship quality, size measurements, weight check, functionality assortment, accessories, labeling & logos, packaging, packing and other tests and special requirements, depending on the product and the export market.
Production Monitoring
Production Monitoring is a review of the production process to identify weak points that affect the finished goods quality. The objective is to identify and implement suitable corrective actions immediately, then monitor and adjust the quality improvements until the final quality objectives are reached.
Process of production
A series of steps carried out in a specific order to produce consumer goods.
Purchase order
A contractual document from the buyer to the supplier that specifies a description of the goods, and the quantity, price, payment terms, and delivery date of an order.
Q
Quality Assurance
Surveillance of every stage of the production process to maintain a desired level of quality and meet expected delivery deadlines.
Quantity Check
One of the main checkpoints during an inspection of consumer goods. It verifies if the number of products manufactured up until a particular stage of production aligns with that required for the final purchase order quantity. For example: If the process is 80% complete, 80% of the total number of products required should also be complete.
Quality Control
The process by which organizations identify nonconformities or defects at each production stage in their supply chain, to avoid delivering goods to consumers which don’t meet their quality expectations.
Quality control strategy
A quality control strategy is an organization’s long-term plan defining what quality control processes they will implement to reach their quality objectives.
Quality Management System
A quality management system documents all information related to an organization’s processes and procedures required to control quality. Most quality systems are based on international standard ISO 9001.
R
Random Sampling
This is a standard sampling method by which random samples of units are chosen such that all combinations of these units have an equal chance of being chosen as the sample.
Regulations
A rule or a directive set by an official authority, government, or trade union that regulates the commercialization of consumer goods within a market and limits the risk of injuries and death that could be caused by the products.
Rejected shipment
A rejected shipment is the result of an inspection FAIL. The buyer does not accept the goods and refuses to ship them to the destination country.
Reduced Inspection
Reduced inspection under a sampling plan uses the same quality level as for normal inspection but requires a smaller sample for inspection. This method is appropriate when the client is confident that the quality of the products is acceptable.
Rejection Number
The rejection number is the minimum number of defects or defective units in the sample that will cause rejection of the lot represented by the sample.
Representative Sampling
Representative sampling ensures that the number of units in the sample shall be selected in proportion to the size of sub-lots or sub-batches, or parts or the lot or batch, identified by some rational criterion. When representative sampling is used, the units from each part of the lot or batch shall be selected at random.
Resubmitted Lots or Batches
Unacceptable lots or batches will be resubmitted for re-inspection only after all units are re-examined or retested and all defective units are removed, or defects corrected. The responsible authority shall determine whether normal or tightened inspection shall be used and whether re-inspection shall include all types or classes of defects or only the particular types or classes of defects which caused initial rejection.
Root cause
The root cause is the origin of a workmanship defect or non-conformity. Identifying the root cause helps to define the appropriate corrective actions.
S
SAI.
Social Accountability International is a global non-governmental organization founded in 1997. SAI’s vision is of decent work everywhere – sustained by an understanding that socially responsible workplaces benefit business while securing basic human rights.
SA8000
SA8000 is a way for retailers, brand companies, suppliers, and other organizations to maintain just and decent working conditions throughout the supply chain. SA8000 is based on international workplace norms in the ILO conventions and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the Convention on Rights of the Child.
It covers Child Labor; Forced and Compulsory Labor; Health and Safety; Freedom of Association and Right to Collective Bargaining; Discrimination; Disciplinary Practices; Working Hours; Remuneration; Management Systems.
SA8000 has achieved considerable awareness internationally. However, most companies have found its requirements to be very strict and have decided not to go for certification. Nevertheless, many have found it to be useful as a guidance document and have claimed unofficial conformance with its requirements.
Sample
A sample consists of one or more units of product drawn from a lot or batch. The sample units are selected at random without regard to their quality. The number of products in the sample is the sample size.
Sample Size
The number of pieces under scrutiny during a product inspection. It varies depending on the total order quantity and the level of assurance required. International standard ISO 2859-1 has defined procedures for determining the appropriate sample size.
Sampling
The process of taking samples from the production batch to be inspected. A sample consists of one or more units of product drawn from a lot or batch, the units of the sample being selected at random without regard to their quality. The number of product in the sample is the sample size.
Sampling Plans
A lot sampling plan is a statement of the sample size or sizes to be used and the associated acceptance and rejection numbers.
Severity of Inspection
The severity of inspection concerns the total amount, kind, and extent of inspection specified by the quality assurance provisions established for the unit of product, or as dictated by quality history. The three levels used in international standards are Tightened, Normal and Reduced inspection.
The severity of inspection concerns the total amount, kind and extent of inspection specified by the quality assurance provisions established for the unit of product, or as dictated by quality history.
Single Sample Plan
A single sampling plan is a type of sampling plan by which the results of a single sample from an inspection lot are conclusive in determining acceptability. The number of sample units inspected shall be equal to the sample size given by the plan.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a methodology that aims to improve processes to eliminate the probability of defects, improve quality, and reach the highest levels of consumers satisfaction.
Specifications
Specifications are the information provided by the buyer to define the product’s physical and mechanical properties, along with expectations in term of quality (acceptable or non-acceptable defects), packaging, labeling and more.
Standards
Standards are documents setting out specifications, procedures, and guidelines. They are designed to ensure products, services and systems are safe, reliable, and consistent.
Standards provide a framework for determining what level of quality a product should achieve and how that will be judged. A standard can refer to dimensions, functionality, or safety requirements. They are usually defined by official entities, governments, and trade unions.
Subcontractor
An intermediary supplier manufacturing finished goods on behalf of another supplier.
Supply Chain
A system put in place which aims to deliver a specific product to the end consumers. It involves sourcing, manufacturing, quality control, and transportation activities.
Supplier
An organization in charge of manufacturing or supplying a specific product to another organization.
Supplier Audit
See Factory audit.
Surveillance program
A set of quality control actions put in place to monitor and improve the quality of the manufactured goods.
T
Third party QC
An organization that provides a neutral assessment of goods and suppliers by performing product inspections and supplier audits. They do not have any sourcing activity so as to avoid any conflict of interest.
Tightened Inspection
Tightened inspection under a sampling procedure plan uses the same quality level as for normal inspection, but has more stringent acceptance criteria, and therefore more samples must be checked. It is used for high-value products or if there is a history of poor quality.
Time-to-market
It is the length of time it takes from the product being conceived and manufactured until the item is available for sale to end consumers.
Tolerance levels
It is the margin of error accepted by the buyer regarding deviations between the product specifications and the finished goods.
Trading company
An intermediate company responsible for sourcing suppliers, negotiating terms and following up the manufacturing process until shipment.
U
Unit of Production
The unit of product is the thing inspected in order to determine its classification as defective or non-defective or to count the number of defects. It may be a single article, a pair, a set, a length, an area, an operation, a volume, a component of an end product, or the end product itself. The unit of product may or may not be the same as the unit of purchase, supply, production, or shipment.
V
Vendor
An organization that provides goods to other organizations but may not necessarily be the manufacturer of the products.
W
Workmanship
The result of skills used by workers to manufacture a product.
Z
Zero defects
A requirement for a product to have NO defects for it to be compliant and acceptable.